- Total $0.00
How to Identify a Sapphire : Part 2
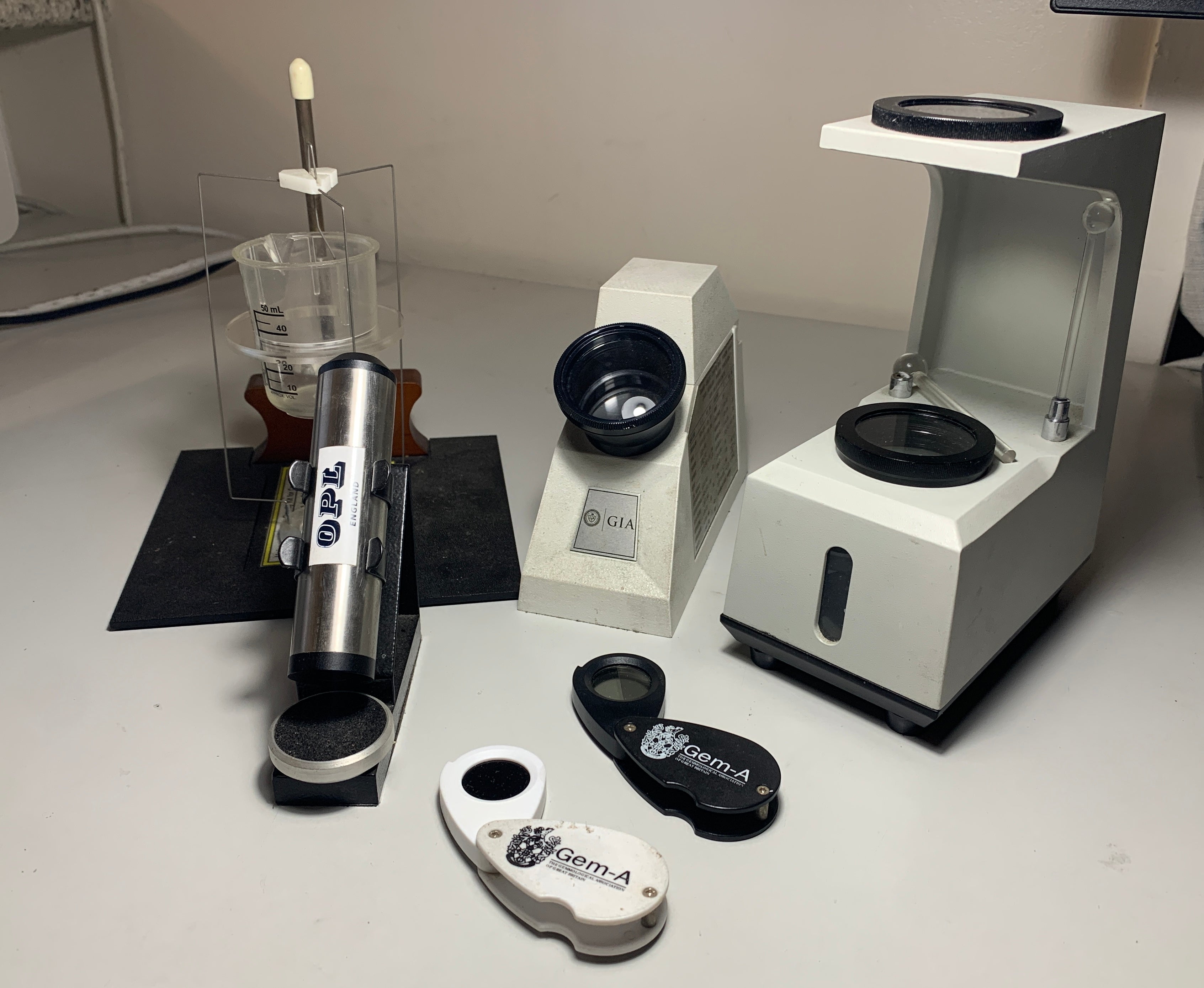
This article serves as the second installment in the "How to Identify a Sapphire" series. Here, we delve deeper into the gemological tools and tests crucial for precise sapphire identification. Each tool mentioned is a staple in every gemologist's toolkit. While accessible to every reader, mastering the use of these tools requires some learning.
As mentioned in Part 1, no single test can definitively identify natural sapphire or any other gemstone. Instead, it's akin to detective work, piecing together clues until a conclusive verdict is reached.

Hardness
Gemstones are categorised based on their Mohs hardness, which measures a material's resistance to abrasion or scratching. However, hardness alone doesn't guarantee toughness or durability. Devised by Friedrich Moh in 1812, the Mohs scale assigns minerals a rating from 1 (very soft) to 10 (very hard). NB!
When Mineral A can scratch Mineral B, Mineral A ranks higher in hardness than Mineral B. For example, if we suspect a stone to be sapphire, we can use a topaz with a hardness of 8 to attempt scratching the stone. If the stone is scratched, it cannot be sapphire. Conversely, if it remains unscathed, it's highly likely the stone has a hardness of 8 or above.
NB! This test is considered destructive and should only be utilised as a last resort. It is advisable to employ this technique on an uncut piece of gemstone to minimise potential loss or damage.

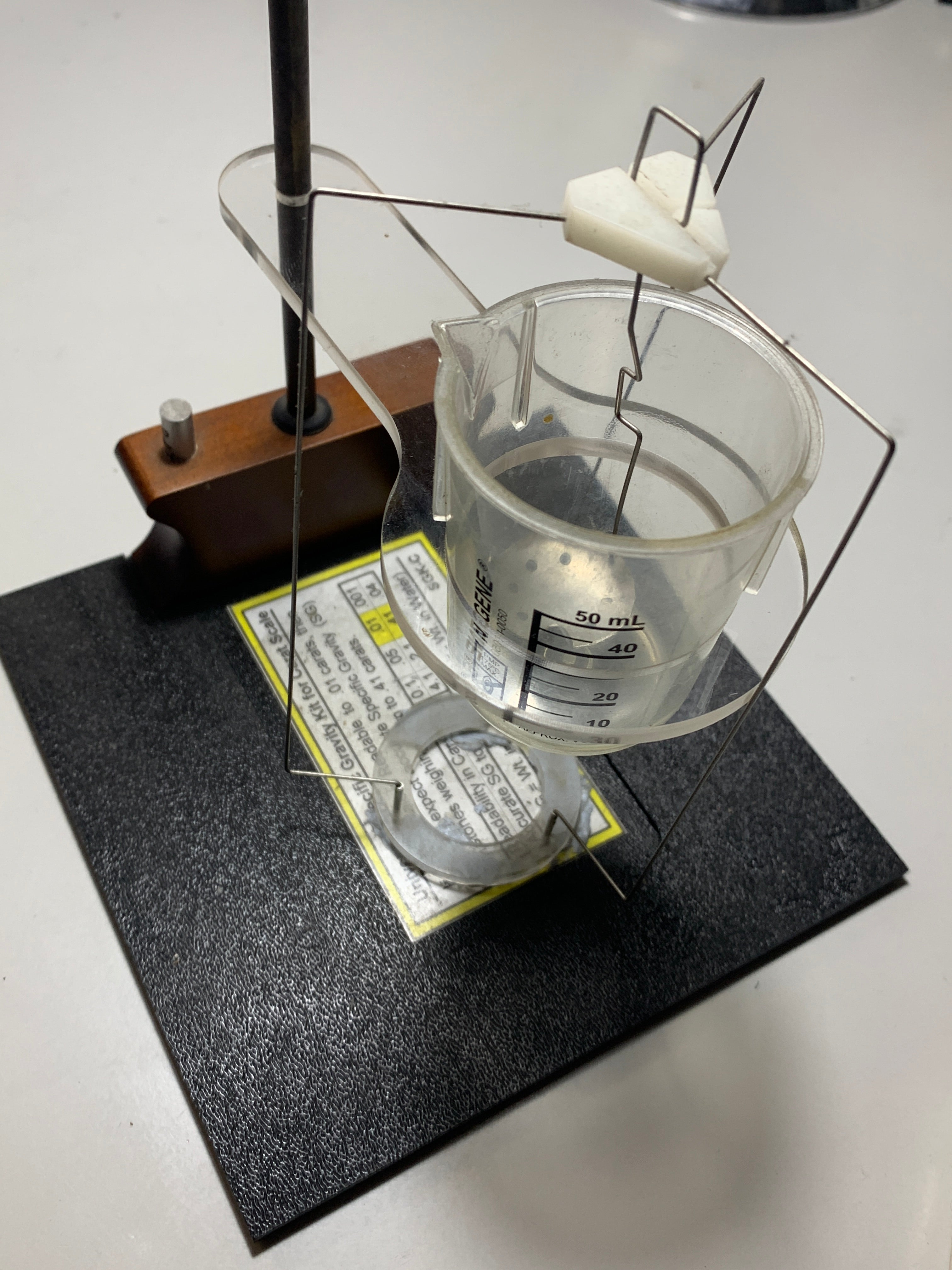
Specific Gravity
The specific gravity test is a method used to determine the density or specific gravity of a gemstone. This test compares the weight of a gemstone in air to its weight when submerged in water. By measuring these two weights, gemologists can calculate the specific gravity of the gemstone, which can be useful for identifying and distinguishing different types of gemstones. It is important to note that sapphire can easily be ruled out using this test.
Highlighting the test's significance, it's worth noting its utility. Sapphire, with its notably high specific gravity of 4, stands out as significantly denser than the majority of gemstones, making this test particularly effective.

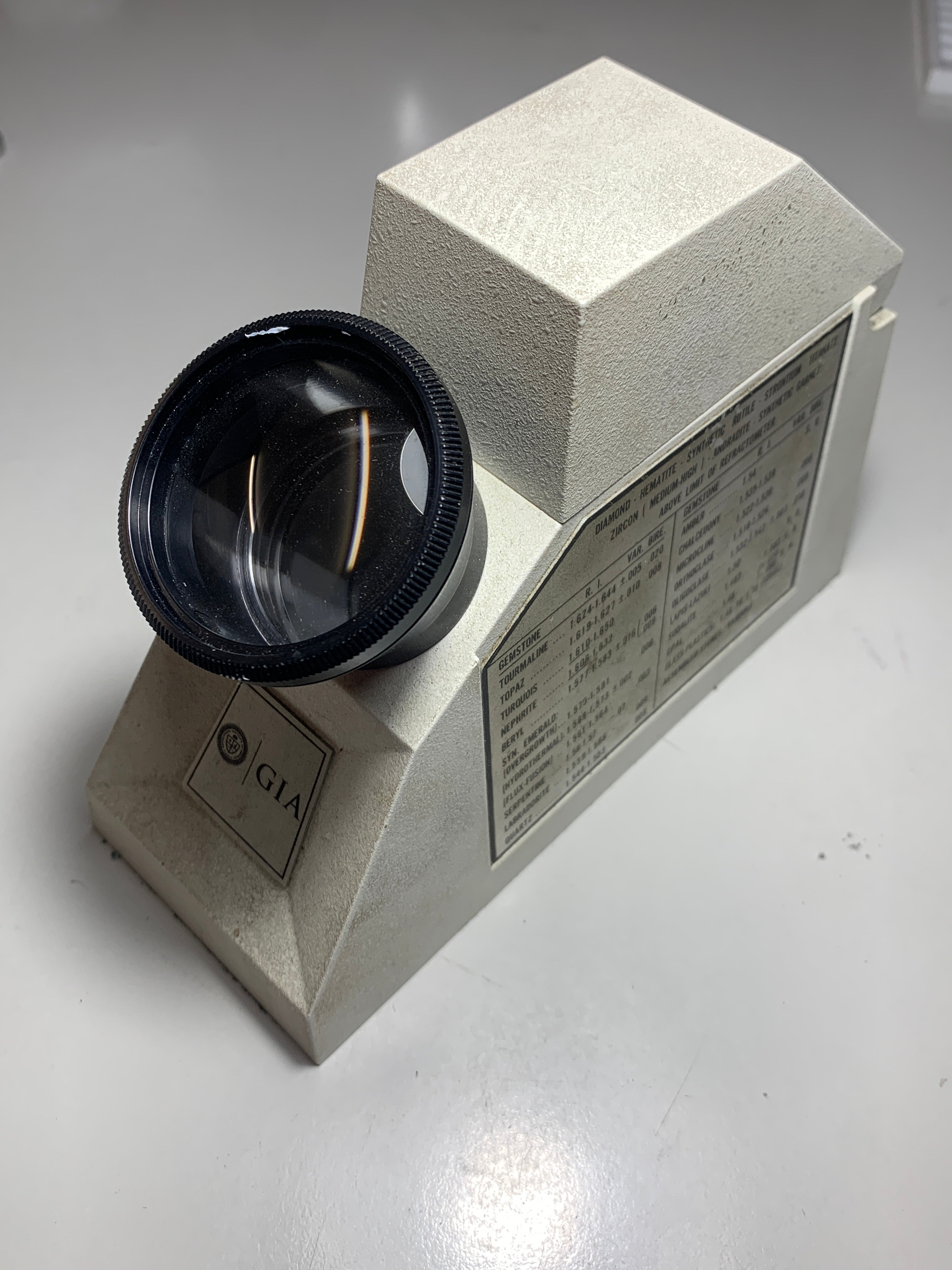
Refractive Index
The refractive index of a gemstone is the degree to which light is bent as it travels through the gemstone relative to its speed in a vacuum. This characteristic is essential for identifying gemstones because each gemstone has its own unique refractive index. Gemologists can often ascertain the identity of a gemstone or at least limit the possibilities by measuring its refractive index.
A Gemological Refractometer is your primary and most powerful tool in gemstone identification. It efficiently gauges the refractive index of faceted stones, from transparent to near opaque varieties.
The refractive index of sapphire typically ranges from approximately 1.760 to 1.770.
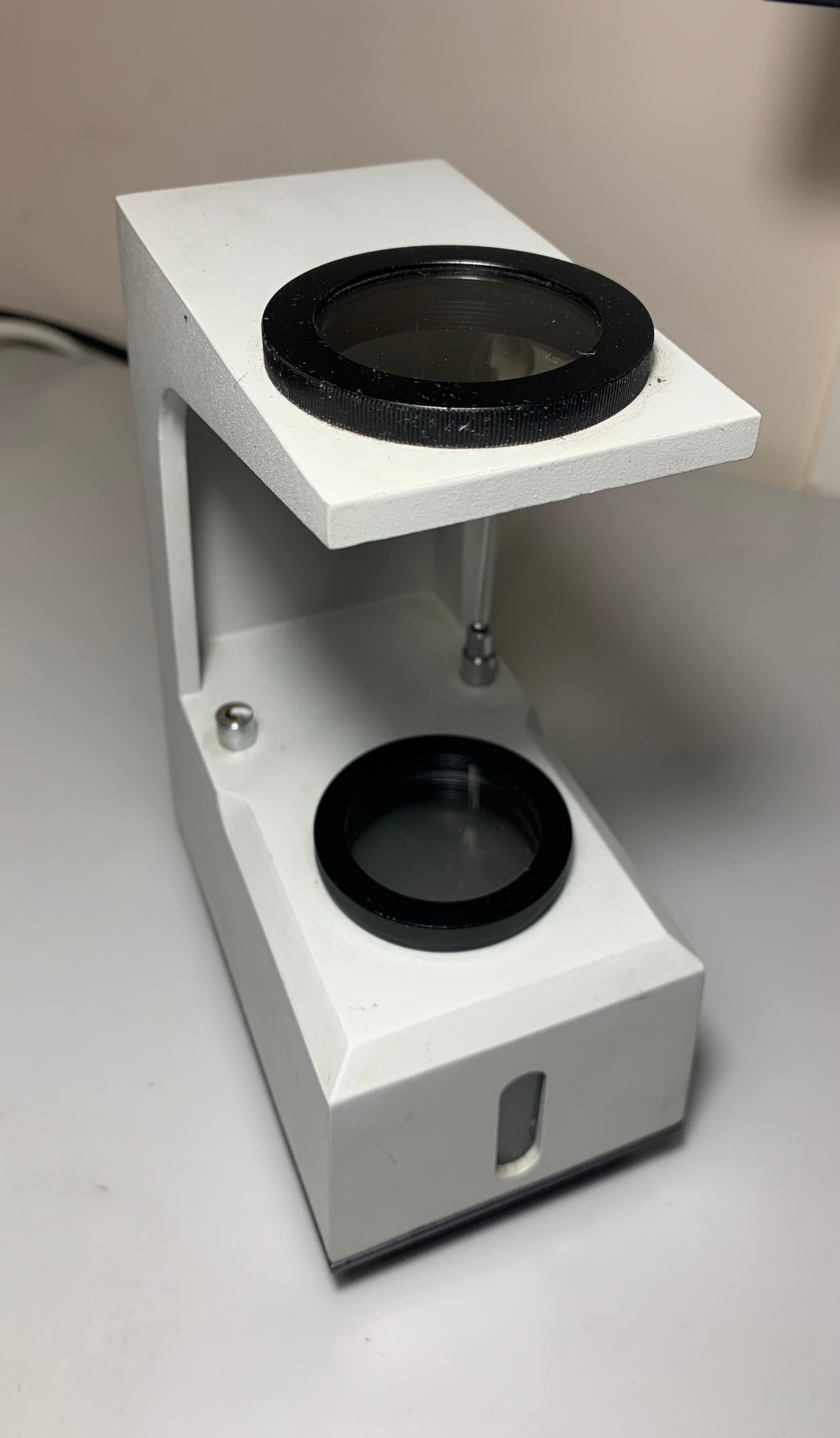
Polariscope
A gemological polariscope is a device used to examine how gemstones react to polarised light. It has two filters that help gemologists observe unique optical properties.
The polariscope is employed to examine the optical traits of gemstones and ascertain if a stone is singly refractive, doubly refractive, or an aggregate.
When observing sapphire under a polariscope, you'll see double refraction, indicating its anisotropic nature.

Dichroscope
A dichroscope is a specialised tool used in gemstone identification. It helps gemologists examine the pleochroism of a gemstone,( Explained in Part 1) which is the ability of a mineral to display different colours when viewed from different crystallographic directions.
Although the dichroscope doesn't directly identify sapphire, it's an invaluable tool for providing additional insights into the crystal structure of the gem being observed. It aids in distinguishing between gemstones with single and double refraction. Sapphire is doubly refractive, it consistently displays multiple shades of colours when examined with a dichroscope.

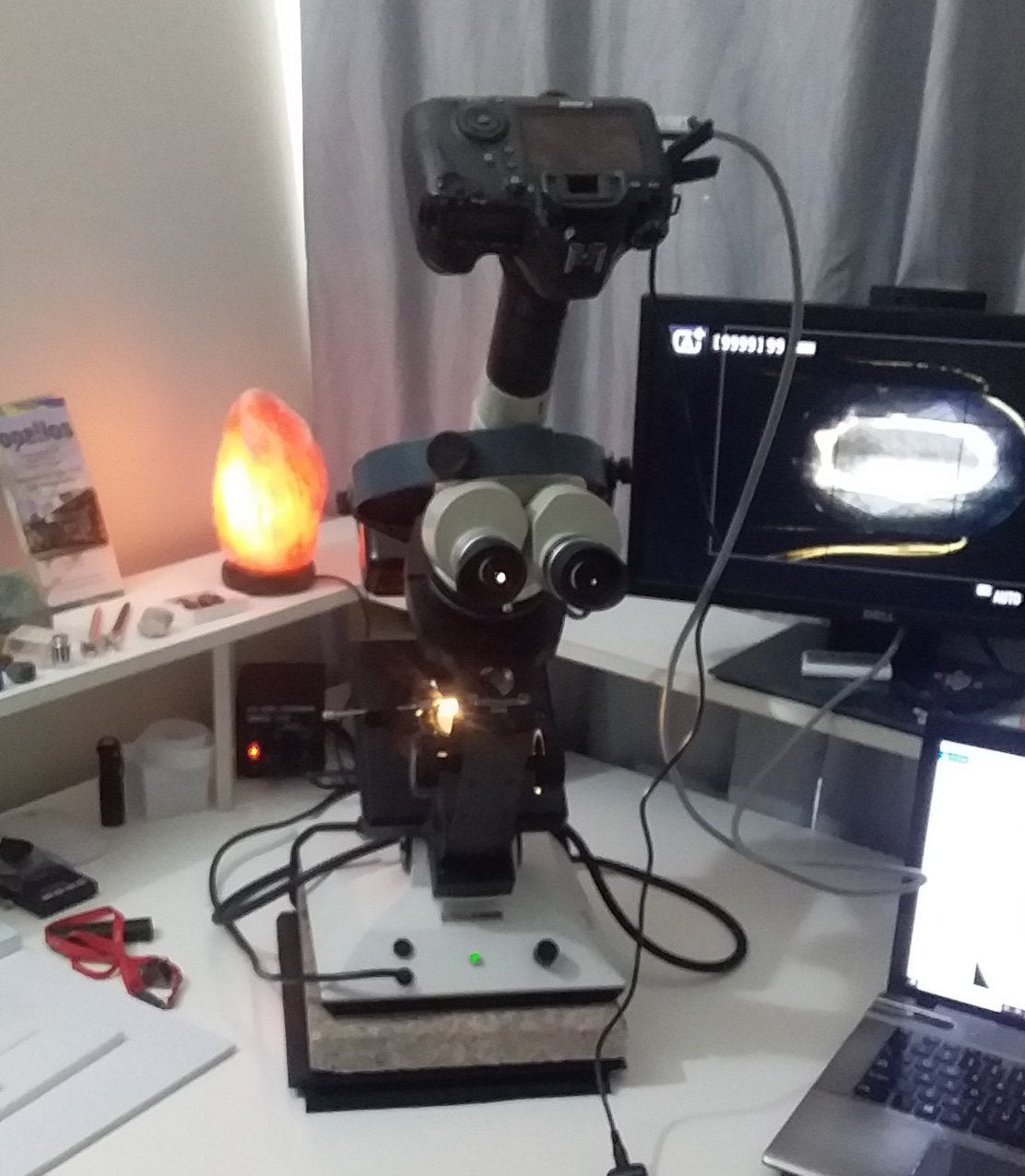
Gemological Microscope
One of the primary uses of a gemological microscope is in the identification of inclusions, flaws, and other internal characteristics within gemstones. Inclusions can provide valuable information about a gemstone's origin, treatment history, and authenticity.
However, the effectiveness of this technique depends greatly on the expertise and experience of the observer. While a microscope can reveal certain telltale signs of synthetic production, such as growth patterns or inclusion types, the interpreter must possess a deep understanding of these features to draw accurate conclusions.
Of all the tools discussed, the microscope stands out as the sole instrument capable of effectively distinguishing between synthetic and natural gemstones, particularly in cases where sapphires have been subjected to heat treatment.

How to Identify Gemstones Part 2
Gemstones are ranked according to their Mohs hardness. Mohs hardness refers to a material’s ability to resist abrasion or scratching. Although a hard gem is not automatically tough or durable. It was devised by Friedrich Moh in 1812, the scale grades minerals on a scale from 1 (very soft) to 10 (very hard).
Remember the difference between the hardness of a diamond and that of a sapphire, is much greater than the scale suggests – diamond at (10) is about 4-5 times harder than sapphire (9), which is about 2 times harder than topaz (8). So it’s a guide – to know which stone is harder, but not by how much.
When Mineral A can scratch Mineral B, Mineral A will rank higher than Mineral B.
For example we assume the stone to be sapphire. we can take topaz hardness 8 and scratch the stone being tested. If the stone gets scratched then it cannot be sapphire. However it it does not it is very likely the stone is hardness 9 or over.
-
Specific gravity
In Ancient Greece, King Hieron II of Syracuse wanted to ascertain whether a crown he had commissioned was made of pure gold. Archimedes (c.287-212 BC), a mathematician and inventor, was set the task, and he established the principle of buoyancy, famously while taking a bath: any object wholly immersed in a liquid experiences a force equal to the weight of the volume of liquid it displaces.
apply the SG formula (A/A-W), dividing the weight of the gem in air (A) by the weight of the gem in air minus the weight of the gem in water (A-W
-
Refractive index
A Gemological Refractometer is your primary and most powerful tool in gemstone identification. As with any typical critical angle refractometer, it will measure the Refractive Index of faceted stones, transparent to near opaque, whether loose or mounted (in many cases), up to an R. I. value of 1.81.
A Refractometer is the instrument used to measure refractive index (RI). A refractometer measures the extent to which light is bent when it moves from air into a sample and is typically used to determine the refractive index of a liquid sample
The index of refraction is a numerical value that represents the ratio between the speed of light in a vacuum and the speed of light in a given material. It determines how much the direction of light changes as it passes through a medium, such as air, water, or glass.
-
Polariscope - negative and positive sign
The polariscope is used primarily to determine the optic character of transparent to translucent gem materials; in other words, it determines whether a stone is singly refractive (SR), doubly refractive (DR), or is an aggregate (AGG). The polariscope is not used with opaque materials.
GIA Polariscope is used to test the optical properties of gemstones and determine whether a stone is singly refractive, doubly refractive or is an aggregate. Doubly refractive stones may be divided further as to whether they are uniaxial or biaxial. The polariscope may also be used to detect pleochroism in doubly refractive colored stones. Diamond cutters use the polariscope to determine the strain characteristics of diamonds.
-
Dichroscope
Dichroscopes are used to look for pleochroism in gemstones to determine if they are doubly refractive gems and will help for gem identification. There are two types of dichroscopes, the Calcite Dichroscope and the Polarizing Dichroscope.
A dichroscope is a pocket instrument used in the field of gemology, and can be used to test transparent gemstones (crystals). Experienced gemologists, observing the pleochroism of some gems, can successfully detect gemstones from other artificial stones using this instrument.
