- Total $0.00
From Tradition to Innovation: How Technology has Revolutionised Jewellery Manufacturing
The untold secrets you have not heard about…
Evolution of the Jewellery Making
Jewellery, an enduring aspect of human culture for millennia, has witnessed the evolution of intricate production methods. From ancient traditions to modern innovations, the journey of crafting adornments reflects not only artistic expression but also technological advancements, changing societal values, and a continuous quest for beauty and self-expression.
The two primary approaches, handmade and cast, result in distinct characteristics for the crafted pieces.

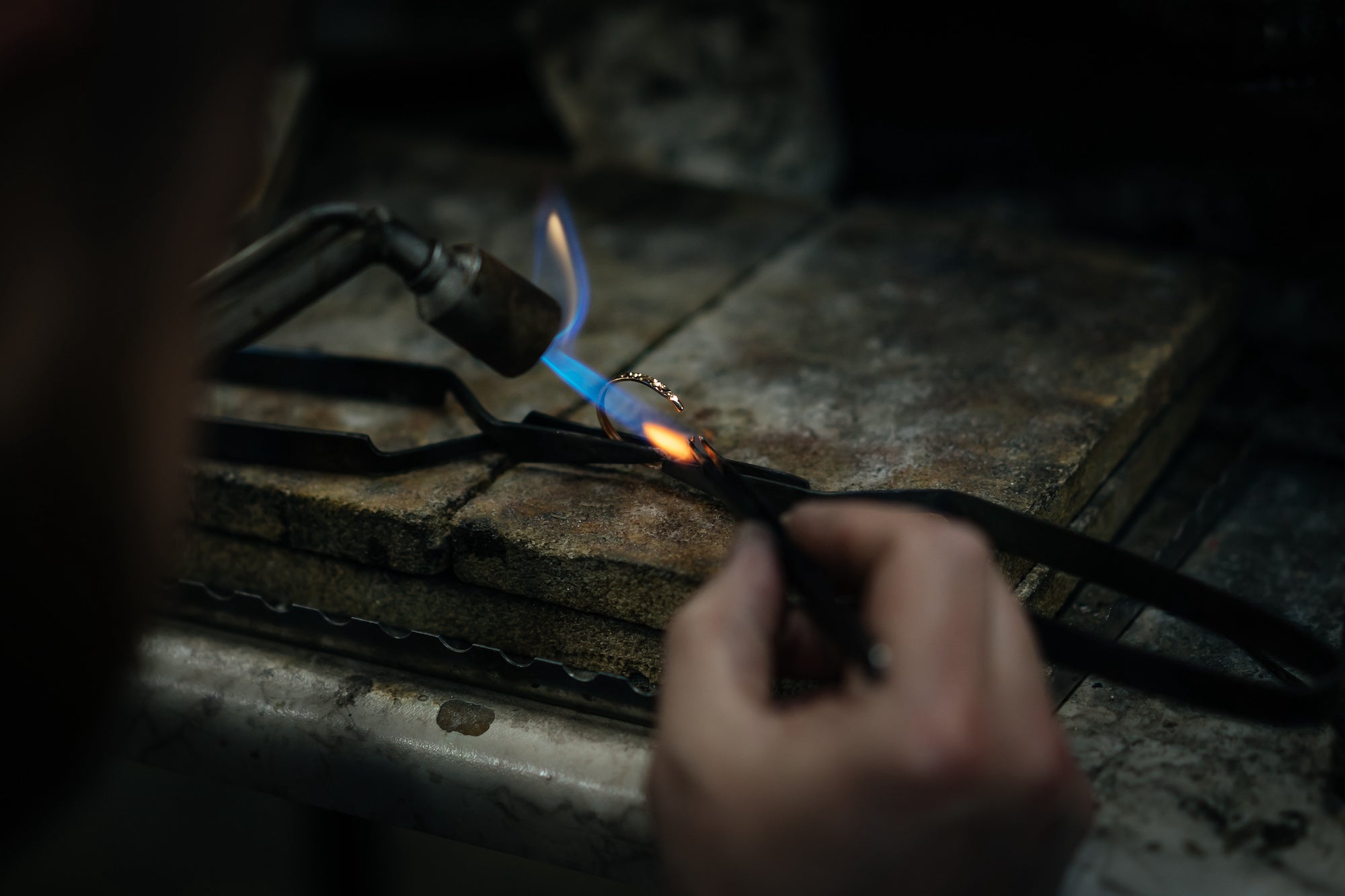
Handmade Jewellery
Handmade jewellery begins with design, followed by careful material selection and metalwork, including shaping, soldering, and stone setting. Artisans use wirework, apply texturing, and add finishing touches before assembling components. The terms "bespoke" and "handmade" refer to different aspects of the jewellery-making process, and while there can be some overlap, they convey distinct concepts:

Bespoke and Handmade?
* Bespoke: Emphasises the customisation and personalised nature of the jewellery, made to order according to the customer's specifications.
It's worth noting that a piece of jewellery can be both handmade and bespoke if it is crafted by hand and tailored to the specific preferences of the customer. However, a piece can also be handmade without being bespoke if it follows a general design or is part of a collection crafted by hand.
Jewellery Manufacturing - Casting
Lost Wax/Resin Casting Process
Lost wax casting, also known as investment casting, is a traditional method for crafting detailed metal objects. The process involves creating a wax model, forming a mould around it, melting out the wax to create a cavity, pouring molten metal into the cavity, and then removing the mould to reveal the final metal object. This technique is prized for its ability to produce intricate shapes, making it popular in the creation of sculptures and jewellery.
There are three main ways models are created: wax carving, wax injection, and resin printing.
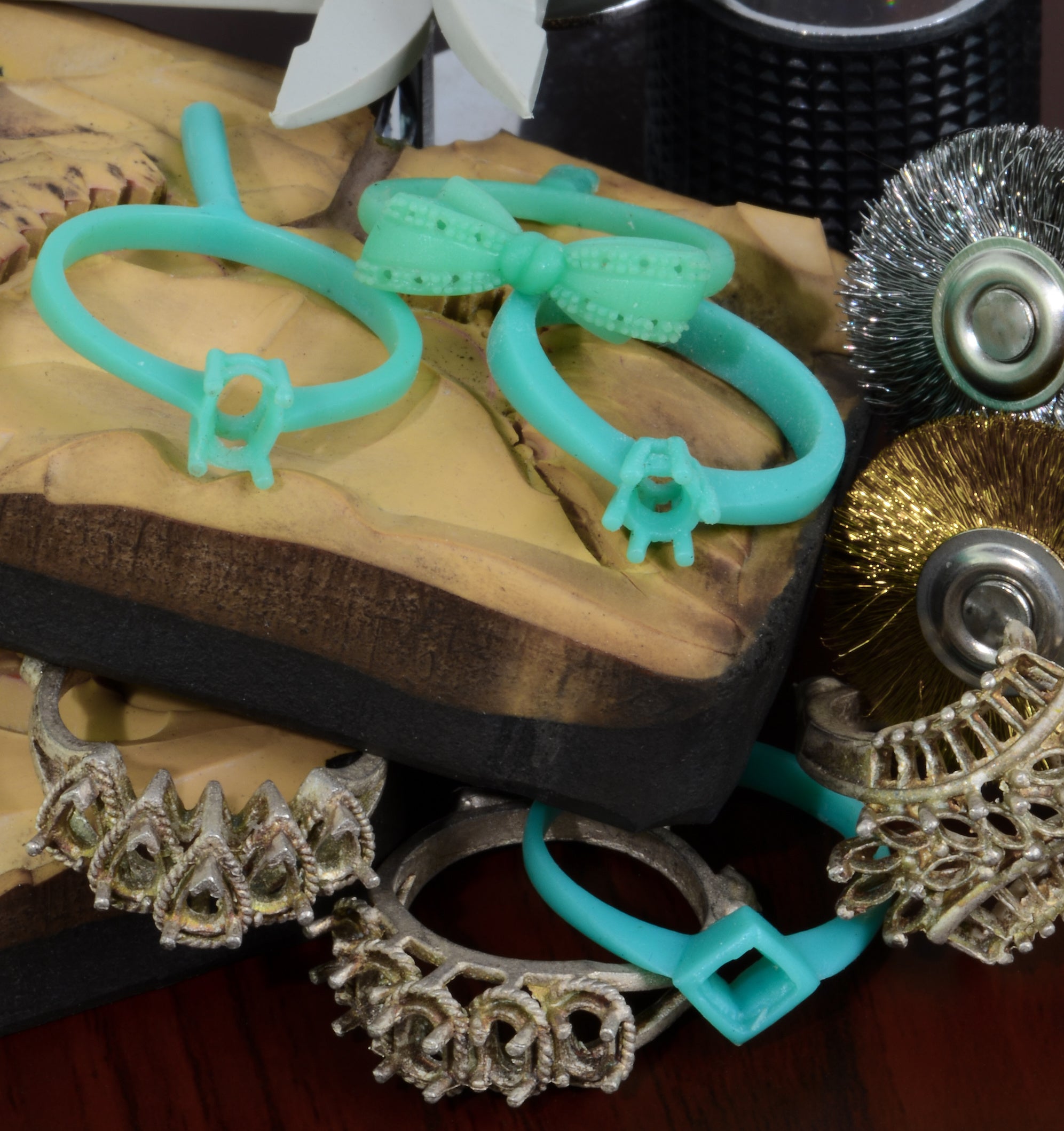

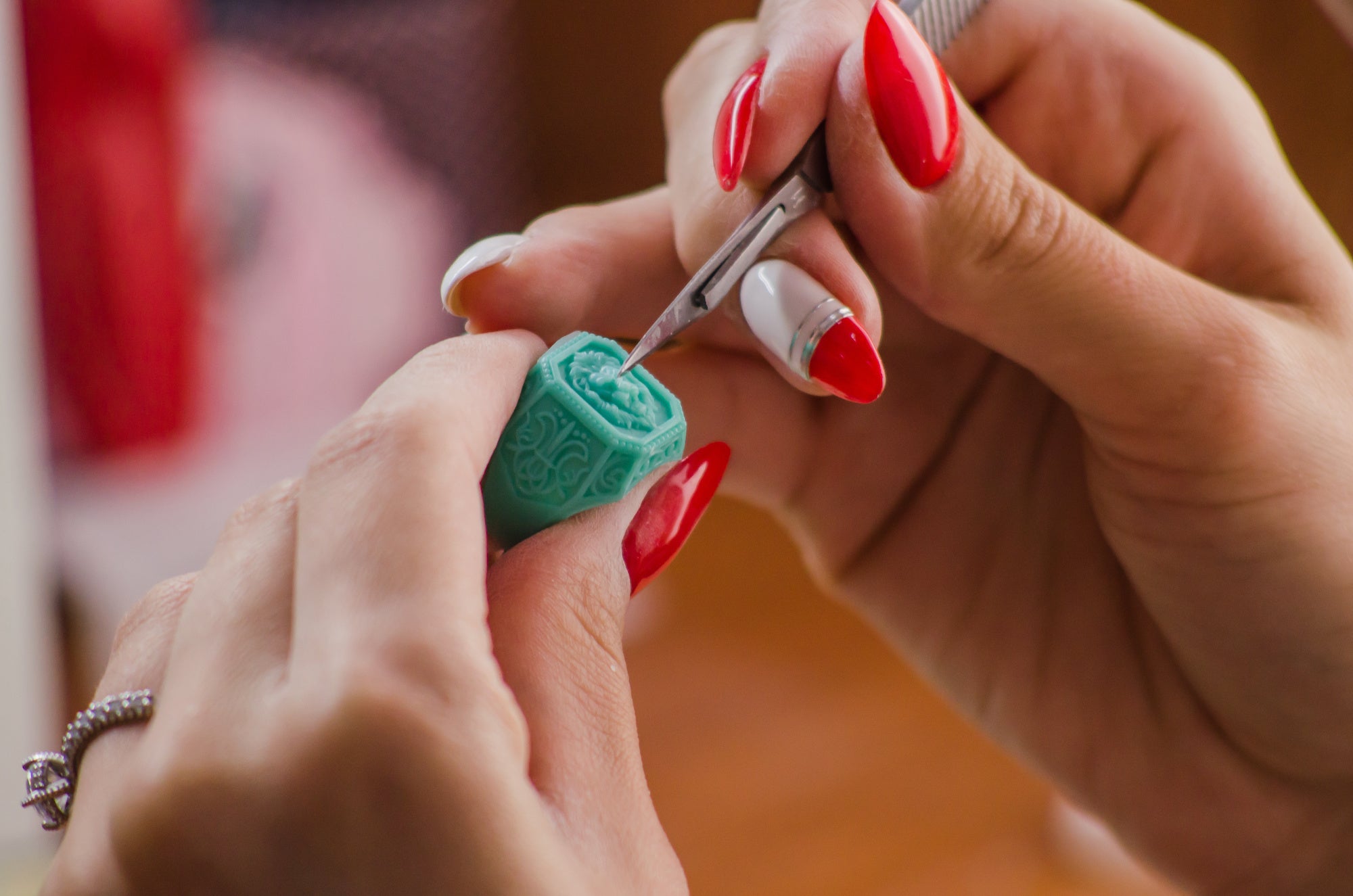
Wax Carving
Wax carving involves shaping three-dimensional objects or designs using wax as the primary material. This method finds applications in various domains, including jewellery crafting, sculpture, and dentistry. Artisans utilise the wax carving process to precisely fashion intricate models before progressing to the final production phase, often incorporating metal casting.

Wax Injection
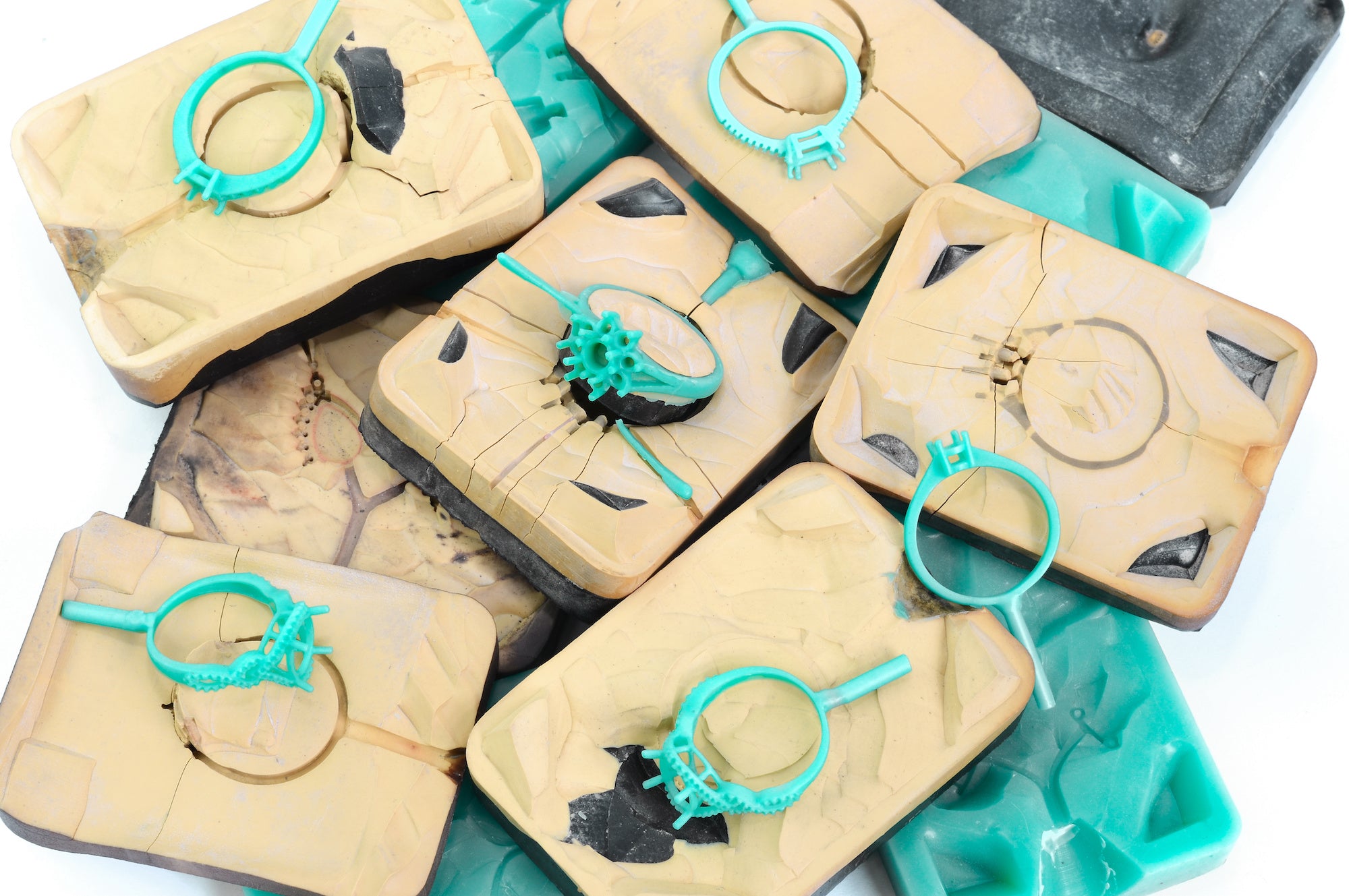
The wax injection process stands as a crucial phase in crafting intricate metal pieces, frequently utilised in both jewellery making and metal casting. This technique involves injecting molten wax into a precisely crafted mould, resulting in the formation of precise wax replicas mirroring the desired object or design. In tandem with wax injection, rubber moulding is commonly employed, where flexible moulds suitable for various casting materials are created.

Computer Aided Design - CAD
Computers have undeniably transformed various industries, and an illustrative instance of this transformation is evident in the application of technology to CAD jewellery design. Artisans utilise cutting-edge equipment and software to craft intricate jewellery designs on computer screens. Subsequently, a CAD file is employed to 3D print a wax model, which is then cast into a precious metal. The 3D printing process offers heightened efficiency compared to manual wax model creation, leading the jewellery industry to increasingly adopt this technology over the last decade.
Understand the Process in 8 Steps
Step 1

Design
1) A hand-drawn jewellery design is a manually crafted representation of a jewellery piece created through the artistic process of drawing, using traditional tools like pencils and pens on paper. This approach allows for a personalised and artistic touch, capturing the designer's vision through pencil or pen strokes.
2) CAD jewelry design employs digital software to precisely model and modify jewelry concepts in 3D. It includes virtual prototyping, reducing costs and time. Rendering tools help designers visualize realistic outcomes for client presentations. Integrated with manufacturing, CAD ensures a smooth transition from digital to physical creation, with digital files allowing easy archiving and version control, streamlining the design workflow.
Step 2

Model Making
1)
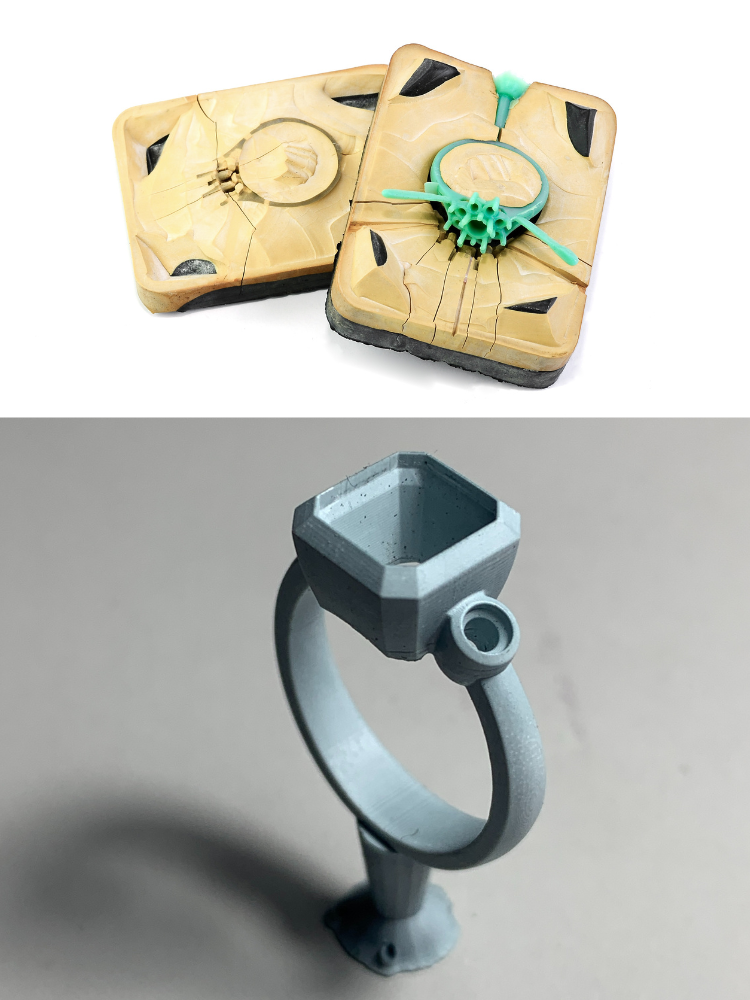
Typically, a jeweller handcrafts a piece of jewellery, which is then employed to produce a rubber mould, subsequently used in the creation of wax models. This mould is then used for wax injection, where molten wax is injected into the mould to form an exact replica of the original design.
2)
CAD revolutionises the realisation of ideas, especially in the context of 3D printing with resin. It commences with a precise digital representation within CAD software. Once refined, the CAD design seamlessly transitions into a tangible form through the intricate process of 3D printing.
Step 3

>
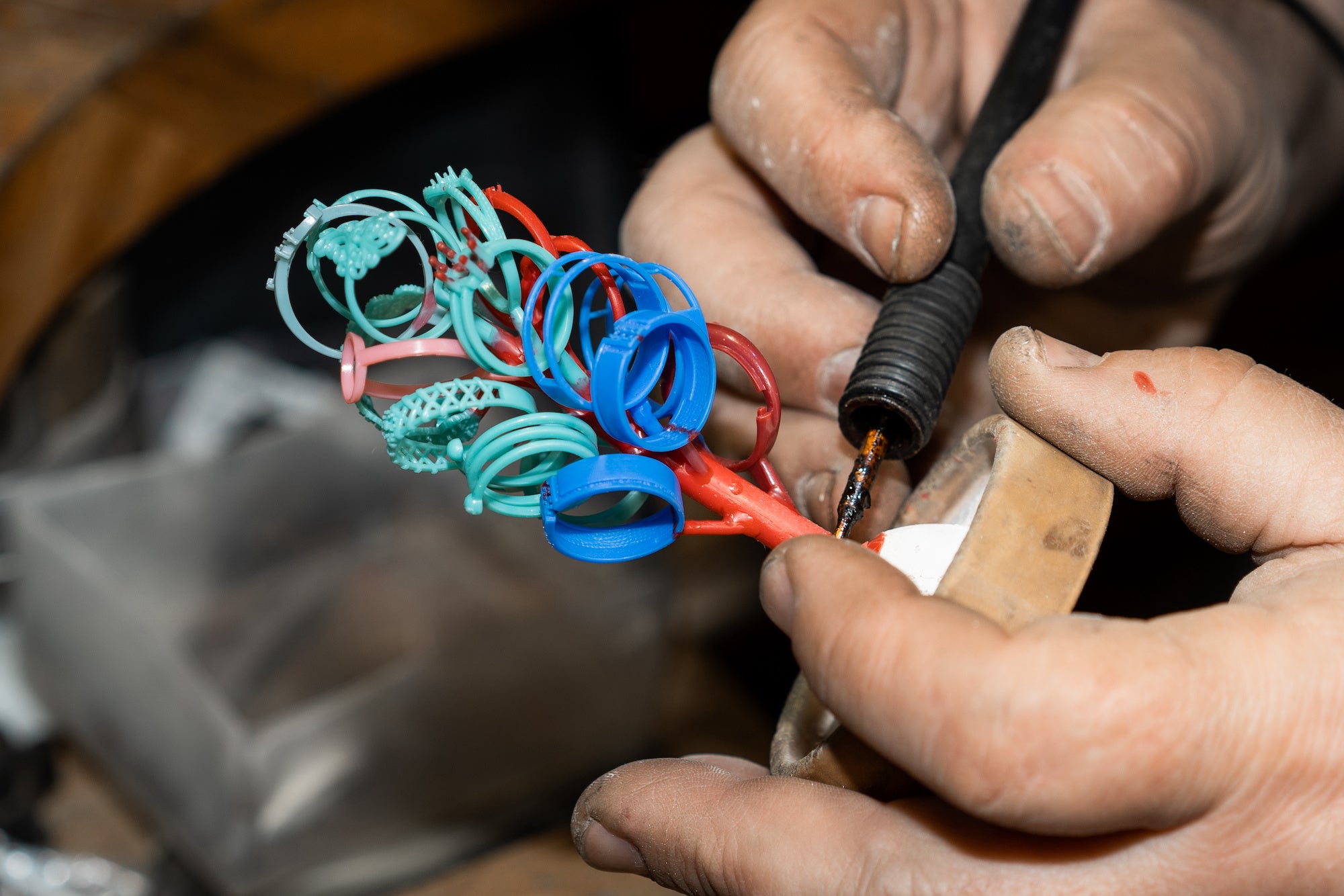
Spruing / Preparing to Cast
This technique involves attaching wax models to a central wax stem, known as a sprue, which serves as a channel for the molten metal to flow into the mold during the casting process. Proper spruing is essential for achieving high-quality castings with minimal defects.
Step 4
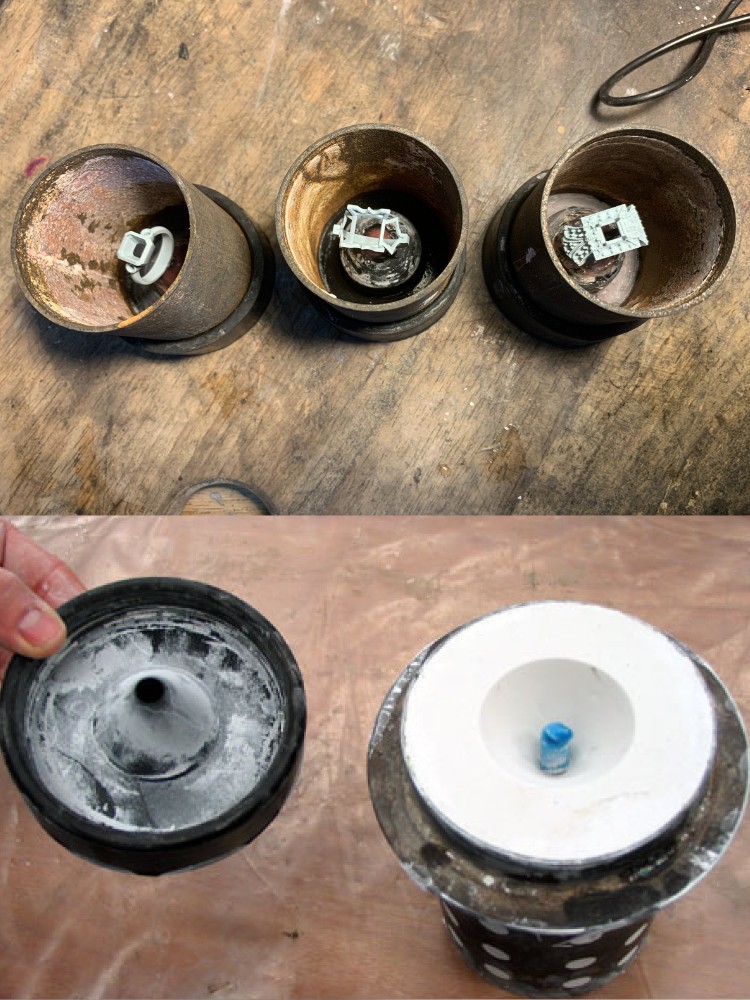

Mould Making/ Investing
This step involves preparing the investment material, a specialised plaster-like substance that forms the mould around the wax model.These flasks are then filled with plaster to remove the remaining space inside before being left to set.
Step 5

Burnout - Wax Elimination
The flasks are positioned in a dedicated kiln where the wax is gradually eliminated. The kiln's temperature increases slowly to ensure the complete removal of wax, preventing any residue. The wax within the investment mould undergoes melting and vaporisation, forming a cavity. The high-temperature burnout process serves to strengthen the mould.
Step 6
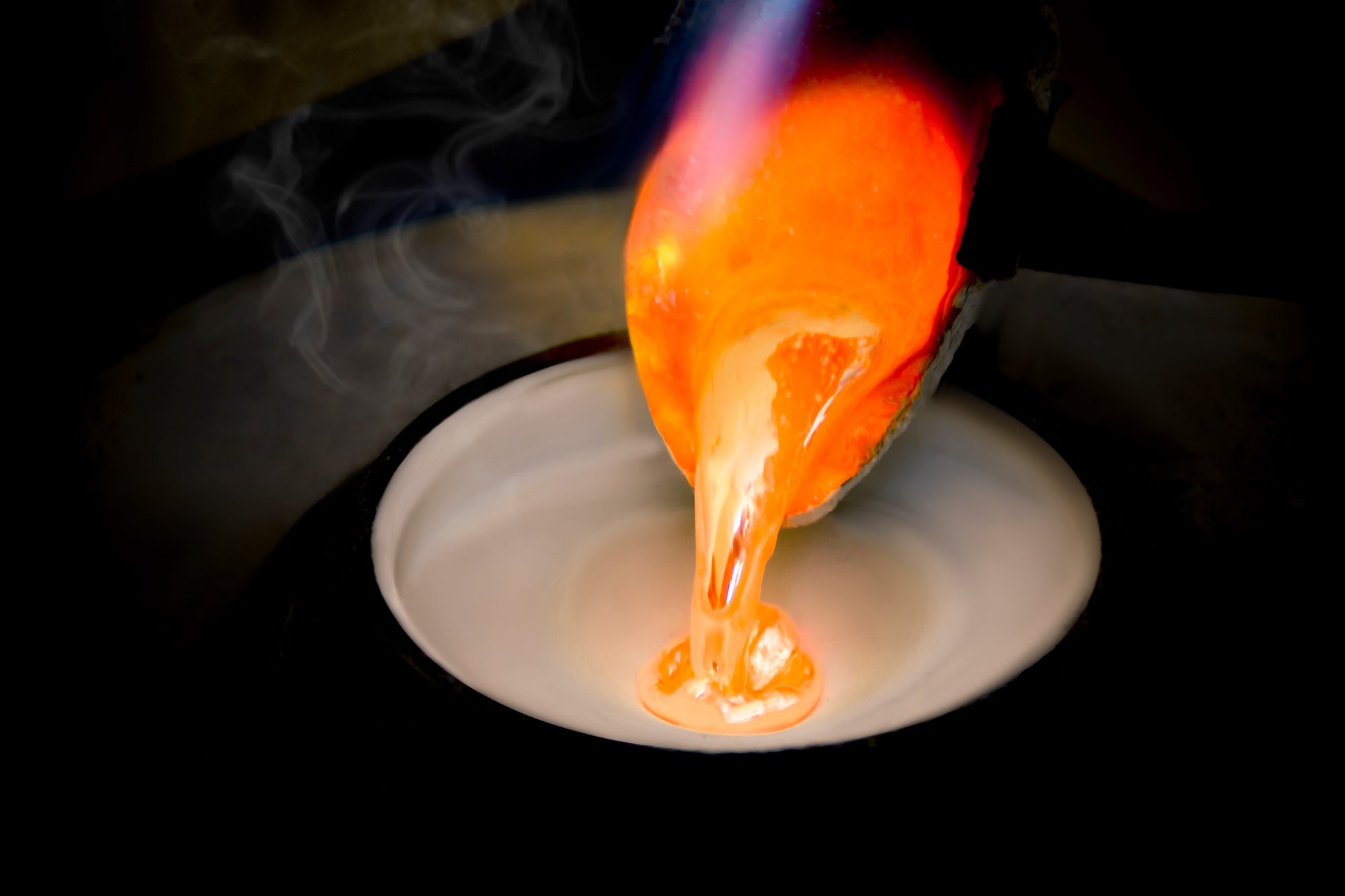

Metal Pouring
Molten metal, often gold or silver, is carefully poured into the prepared mould, filling the cavity.
Step 7
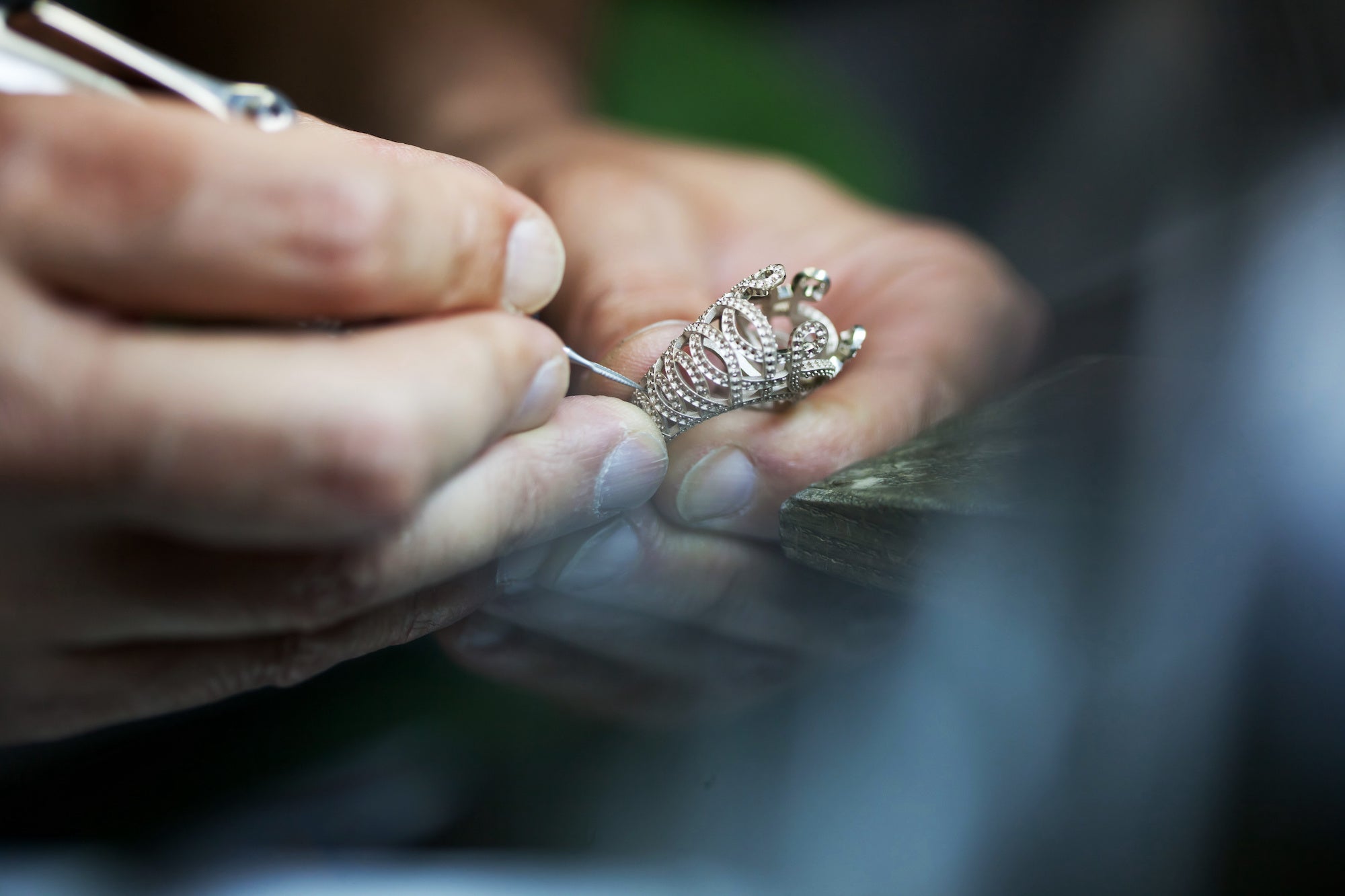

Clean Up/ Polishing
The crafted piece undergoes thorough finishing procedures, including polishing and intricate detailing, to attain its ultimate, refined appearance.
Step 8
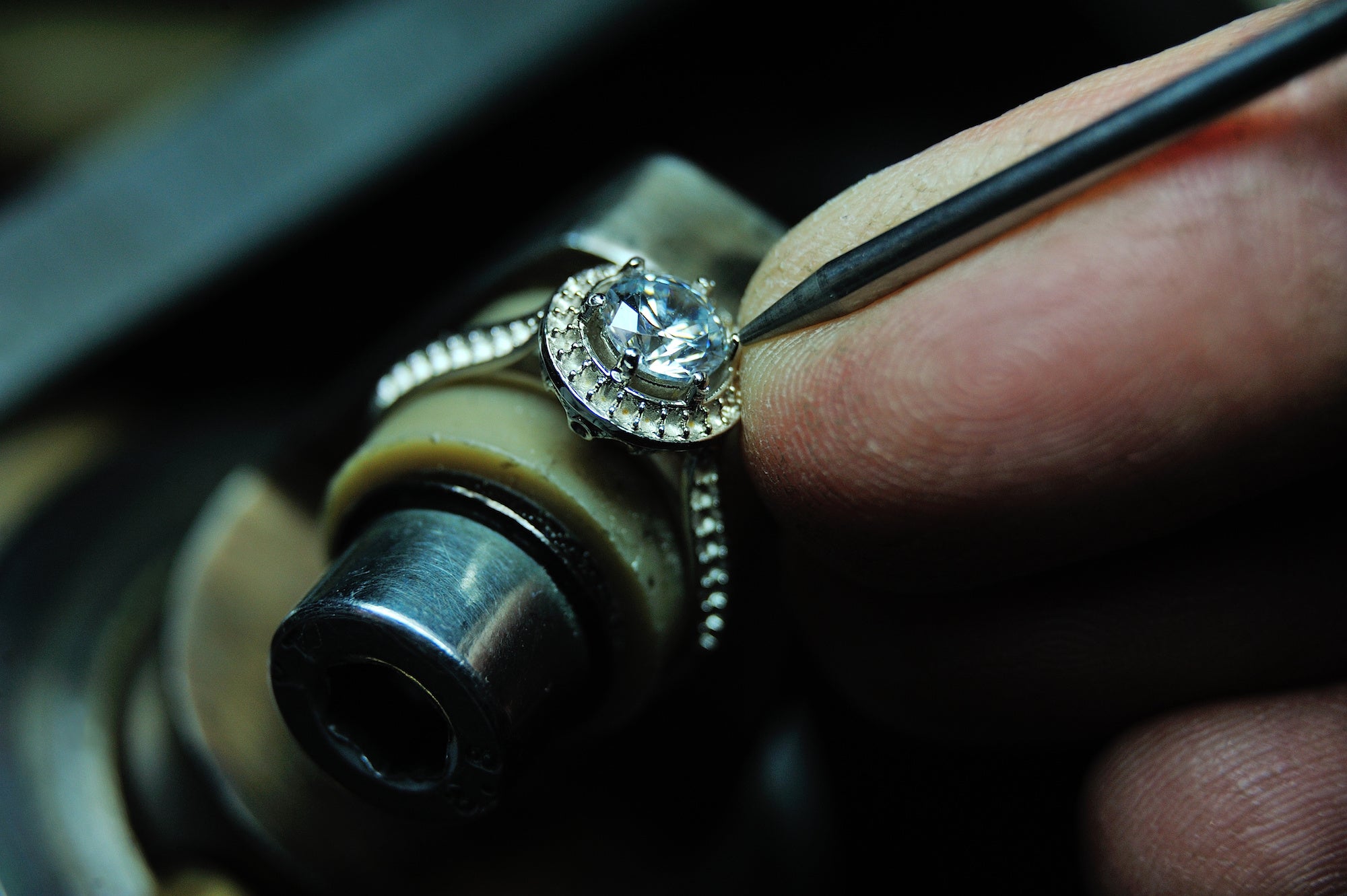

Stone Setting
Stone setting stands out as one of the most demanding and technically intricate tasks in jewellery crafting. Often, the placement of gemstones marks the final stage in the entire process of creating a piece of jewellery. This crucial step involves attaching gemstones securely within a metal casting, adding the finishing touch to the intricate art of jewellery making.
Experience the power of technology and get your dream jewellery creation started today, whether it is an engagement ring, pendant, or a set of earrings - possibilities are endless.
Never before, with state-of-the-art technology, can jewellery be manufactured:
◦ Time efficient - Take no risk of missing the deadline. Jobs can be done in days.
◦ Cost-effective - Keep more money in your pocket, 30 percent cheaper than traditional methods.
◦ Precise - Exceptionally accurate to fit your design ideas or your chosen gemstones.
◦ Predictable - Hassle-free, before production starts, you will be able to see the exact design on the computer and printed in 3D.
◦ Flexible - You can request unlimited changes to the design before production even begins.
Risk-free, send us your message now



